Provisioning updates to managed resources
You can use Lenovo XClarity Orchestrator to maintain current software levels on Lenovo XClarity Administrator resource managers and managed servers. You can use the updates catalog to know what software levels are available, use update-compliance policies to identify which resources need to be updated based on custom criteria, and then deploy the desired updates to those resources.
Procedure
The following figure illustrates the workflow for updating managed resources.
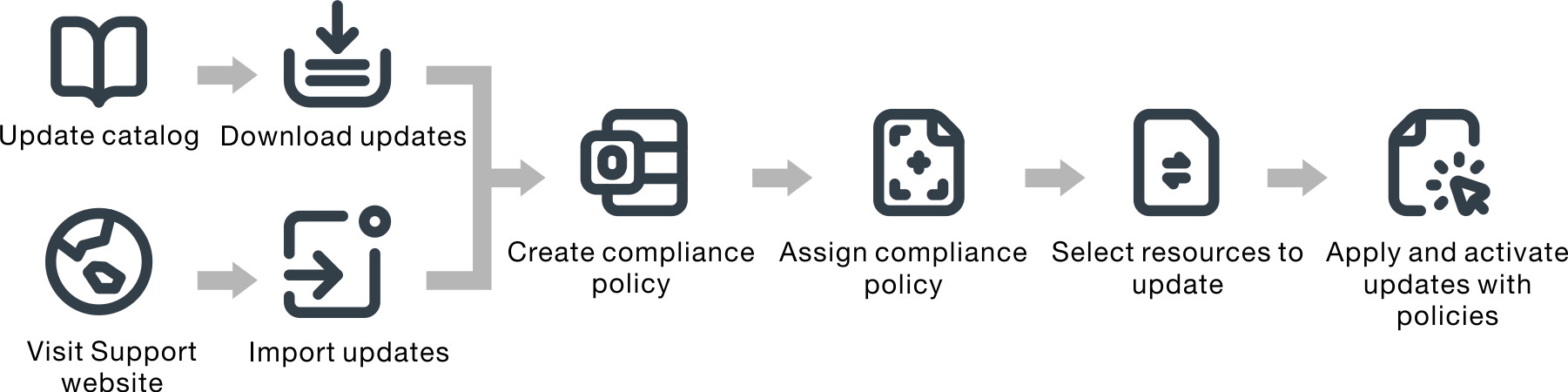
- Update the catalog
The updates repository contains a catalog and the update packages that can be applied to managed resources.
The catalog contains information about updates that are currently available. The catalog organizes the updates by resource types (platforms) and components. When you update the catalog, XClarity Orchestrator retrieves information about the latest available updates from the Lenovo Support website and stores the information in the updates repository.
ImportantXClarity Orchestrator must be connected to the Internet to update the catalog.When new update packages become available, you must import the applicable update packages before you can apply an update. Updating the catalog does not automatically import the update packages.
When XClarity Orchestrator is initially installed, the updates repository is empty.
- Download or import update packages into the repository
If XClarity Orchestrator is connected to the Internet, you can download update packages that are listed in the updates catalog directly from the Lenovo Support website. If XClarity Orchestrator is not connected to the Internet, you can manually import update packages that you previously downloaded from the Lenovo Data Center Support website to a workstation that has network access to the XClarity Orchestrator host.
If you choose to download a minor release, the prerequisite update packages are also downloaded.
When you manually import repository packs, you must import the payload (.tgz), metadata (.xml), change log (.chg) and readme (.txt).
When you manually import updates, you must import the required files base on the resource type.For ThinkSystem V3 servers, import the single update package (*.zip). This zip file contains the payload, metadata files (several *.json files), change log file (*.chg) and readme file (*.txt).
For ThinkEdge Client devices, import the payload (Windows .exe). The readme (.txt) is optional. Note that only the BIOS flash utility package for Windows update is currently supported.
For Management Hub, import the single update-package file (.tgz). This file contains the payload, metadata, change history, and readme files.
For all other resources (including XClarity Administrator, ThinkEdge servers, ThinkSystem V1 and V2, and legacy devices), import the payload (.zip, .uxz, .tar.gz, .tar, .bin), metadata (.xml), change log (.chg) and readme (.txt).
For more information about importing updates, see Downloading and importing updates.
- Create and assign update-compliance policies
Update-compliance policies ensure that the software or firmware on certain managed resources are at the current or specific level by flagging the resources that need attention. Each update-compliance policy identifies which resources are monitored and which software or firmware level must be installed to keep the resources in compliance. XClarity Orchestrator then uses these policies to check the status of managed resources and to identify resources that are out of compliance.
When you create an update-compliance policy, you can choose to have XClarity Orchestrator flag a resource when the software or firmware on the resource is down level.
After an update-compliance policy is assigned to a resource, XClarity Orchestrator checks the compliance status of the resource when the updates repository changes. If the software or firmware on the resource is not compliant with the assigned policy, XClarity Orchestrator flags that resource as not compliant on the Apply / Activate page, based on the rules that you specified in the update-compliance policy.
For example, you can create an update-compliance policy that defines the baseline software level for XClarity Administrator, and then assign that policy to all XClarity Administrator resource managers. When the updates catalog is refreshed and when a new update is downloaded or imported, the XClarity Administrator instances might become out of compliance. When that happens, XClarity Orchestrator updates the Apply / Activate page to show which XClarity Administrator instances are not compliant and generates an alert.
For more information about creating update-compliance policies, see Creating and assigning update-compliance policies.
- Apply and activate updates
XClarity Orchestrator does not automatically apply updates. To update software resources, you must manually apply and activate the update on selected resources that are not compliant with the assigned update-compliance policy.
XClarity Orchestrator does not directly update resources. Instead, it sends a request to the applicable resource manager to perform the update, and then tracks the progress of the request. XClarity Orchestrator identifies the dependencies that are required to perform the update, ensures that the target resources are updated in the correct order, transfers the applicable update packages to the resource manager, and creates a request to start a job on the resource manager to perform the update.
For more information about applying updates, see Applying and activating updates to resource managers and Applying and activating updates to managed servers.
- Update deployment considerations
Before deploying updates using Lenovo XClarity Orchestrator, review the following important considerations. - Downloading and importing updates
Updates packages must be available in the updates repository before you can apply updates to managed resources. - Creating and assigning update-compliance policies
You can create an update-compliance policy based on the acquired updates in the updates repository. You can then assign the policy to one or more XClarity Administrator resource managers or managed servers. - Applying and activating updates to resource managers
XClarity Orchestrator does not automatically apply updates. To update software, you must manually apply and activate the update on selected Lenovo XClarity Administrator resource managers that are not compliant with the assigned update-compliance policy. - Applying and activating updates to managed servers
Lenovo XClarity Orchestrator does not automatically apply updates. To update firmware, you must manually apply and activate the update on selected devices that are not compliant with the assigned update-compliance policy.